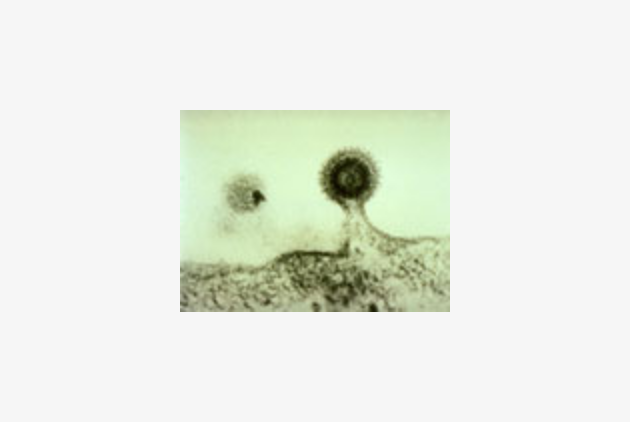
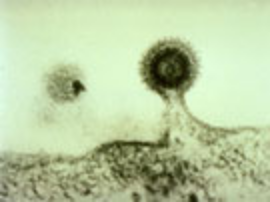
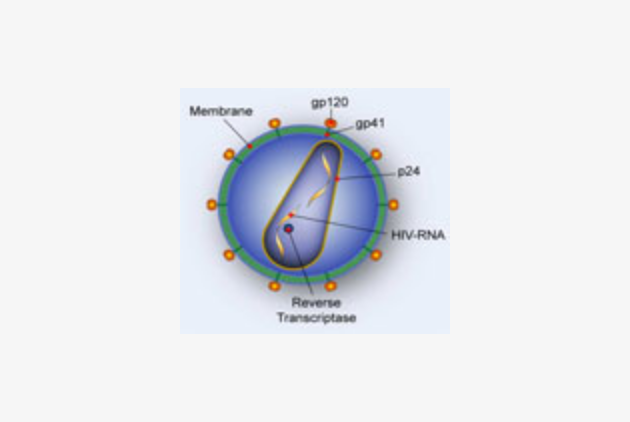
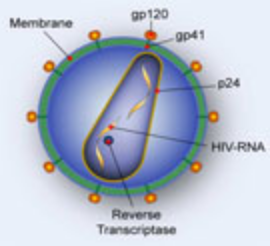
Facts: AIDS stands for "acquired immunodeficiency syndrome." A syndrome is a cluster of medical conditions. AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), which weakens the body's immune system. HIV spreads through unprotected sex (intercourse without a condom), transfusions of unscreened blood, contaminated needles (most frequently for injecting drug use), and from an infected woman to her child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. The majority of infected individuals look healthy and feel well for many years after infection; they may not even suspect they harbor the virus, though they can transmit it to others. A laboratory test is the only way to determine whether an individual is HIV-positive. Once they have an established HIV infection, individuals are infected for life and will probably succumb to serious opportunistic infections. Treatment with antiretroviral (ARV) drugs can slow the progression of HIV infection but there is till no cure for AIDS. Without ARV, the time between HIV infection and the development of AIDS is around 6-10 years, and thereafter most patients die within 2 years.
PREVENTING AIDS
Learn the facts of HIV/AIDS and educate your love ones Practice safe sex (Always Use Condoms) Stop sharing needles and injecting drugs
Mother-to-Child transmission can be eliminated through effective voluntary testing and counseling, access to antiretroviral therapy,
safe delivery practices, and the safe use of breast-milk substitutes Support HIV research to find solutions to end the AIDS crisis
CLICK BELOW TO DOWLOAD INFO-SHEETS FOR
-
Fast facts about HIV (UNAIDS, May 2008)
-
Fast facts about HIV prevention (UNAIDS, April 2008)
-
Fast facts about HIV testing and counselling (UNAIDS)
-
Fast facts about HIV treatment (UNAIDS, June 2008)
Origin and Lifecycle of HIV
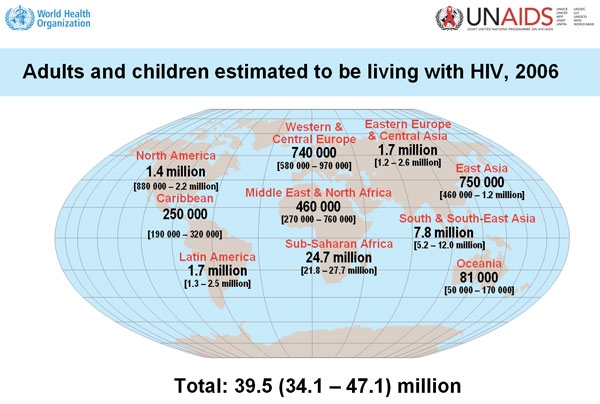
AIDS in the World
In 2007 approximately 4.6 million people became infected with HIV-1 leading to over 33.2 million adults and children living with HIV-1/AIDS in the world. More than 2.1 million are estimated to have died of AIDS in 2007 alone. Although highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) helps to control disease progression and extend the life span of infected individuals in developed countries, HIV-1 infected people in developing countries including China have not gained similar benefits. Up to now, there is still no cure or an effective vaccine for AIDS and there are still many unanswered questions on HIV/AIDS.
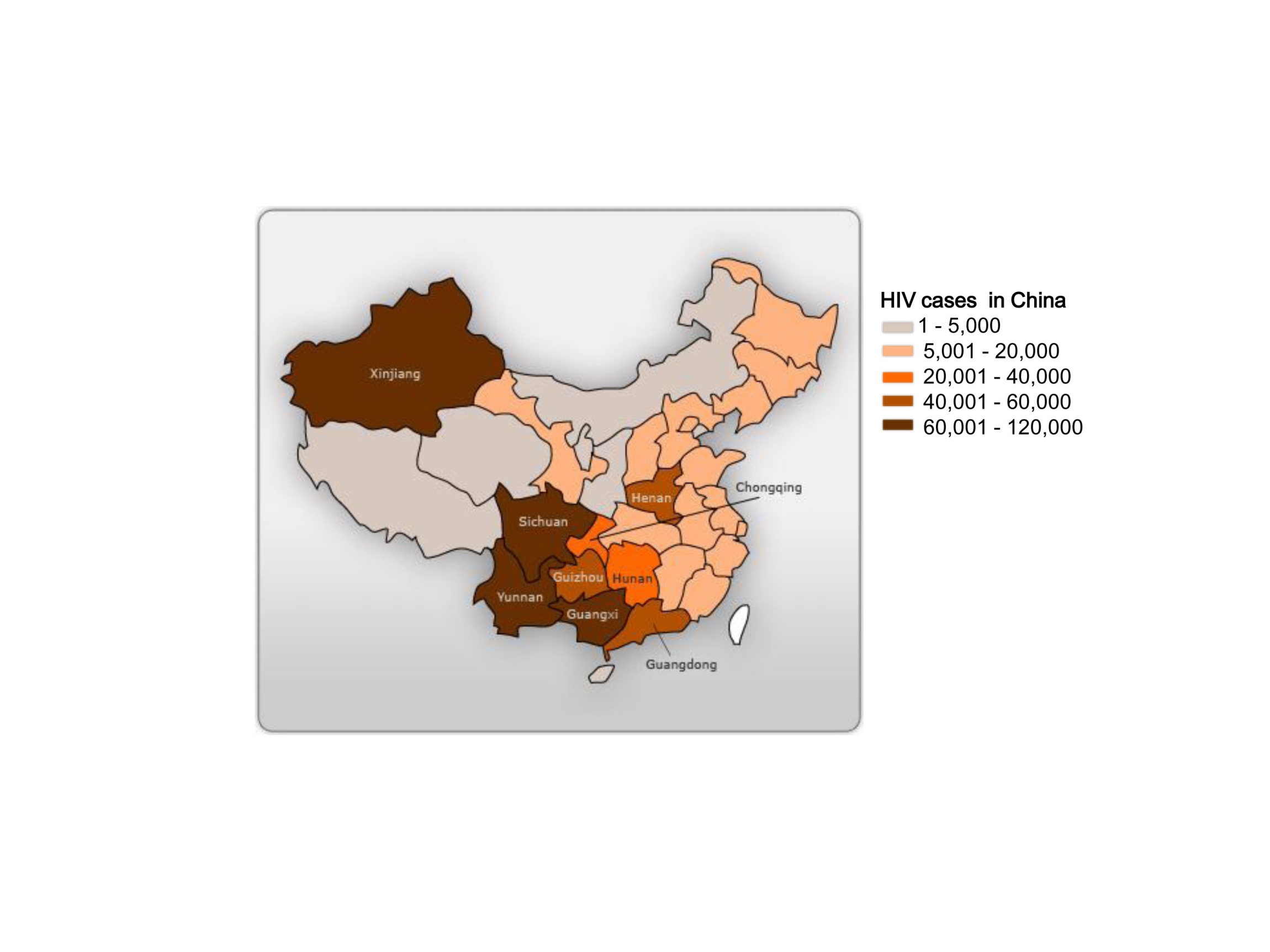
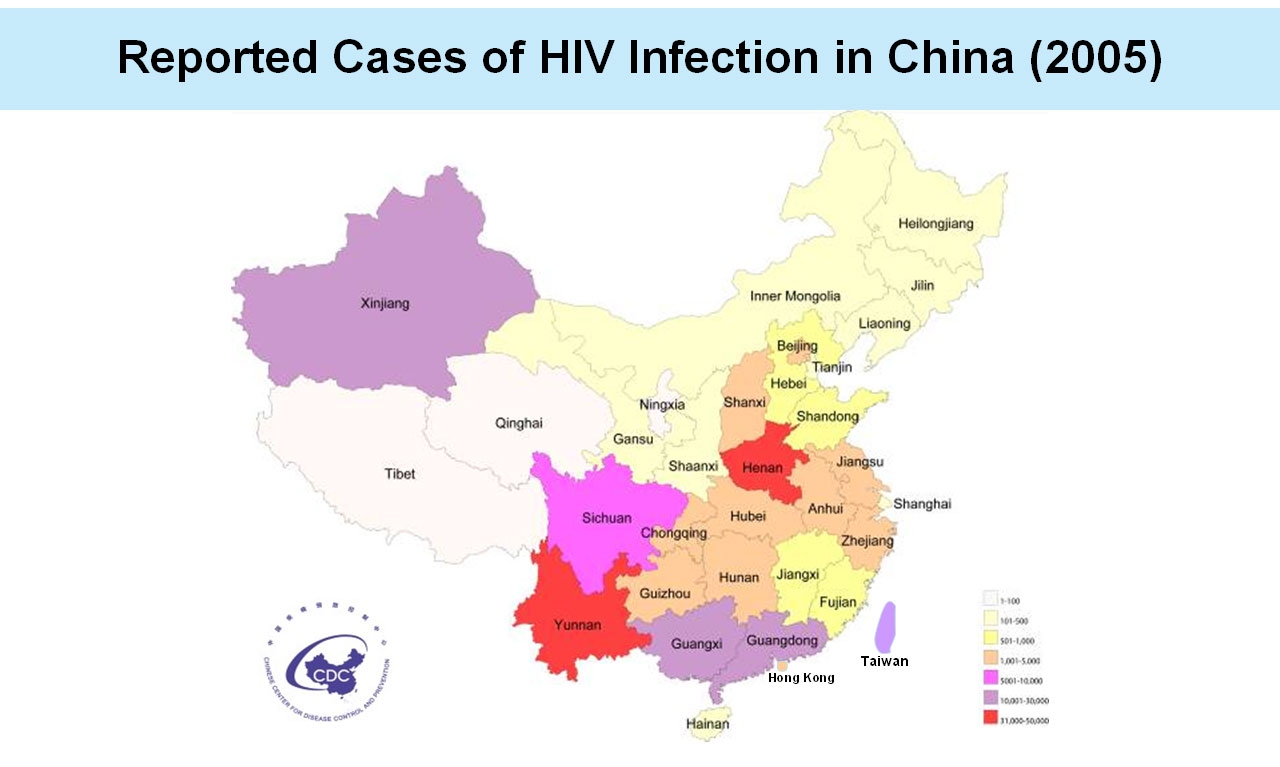
AIDS in China
With the recent evidence that HIV-1 has been transmitted from high-risk groups into the general population mainly through sexual transmission in China(Ministry of Health, China 2006), our nation faces a new challenge to fight HIV/AIDS. Since strategies on HIV-1 prevention and treatment require scientific evidence collected locally, it is important to build an HIV/AIDS research programme in Hong Kong to provide input to enhance the understanding of HIV/AIDS in China.